Polydopamine
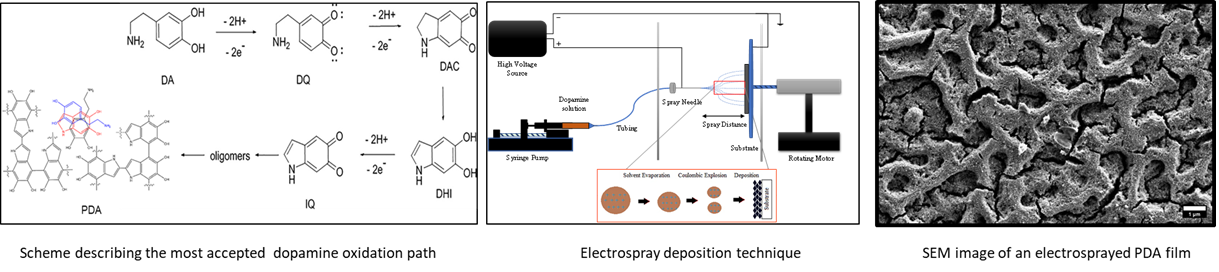
Polydopamine (PDA) is a unique and versatile biomimetic polymer that is obtained when dopamine undergoes oxidative polymerization. The polymerization results in a dark brown or black material that is highly adhesive. The adhesive nature of PDA allows it to coat various substrates, including metals, ceramics. and other polymers, thus enabling a broad range of applications.
In our research, we are focusing on the following topics among many:
- Understanding the fundamentals of dopamine polymerization to PDA: Although PDA has been applied in various fields, its exact structure remains unknown.
- Fabrication of controlled, reproducible PDA films using electrospray deposition: Electrospray deposition is an up-scalable technique that uses high electrical voltage between the spraying needle and the target to atomize a liquid solution to charged droplets, which are guided by the electric field to the target. This minimizes material losses, and allows to control the film thickness, porosity, homogeneity and other properties by adjusting the voltage, solution flow rate, time etc.
- Developing and assessing PDA and related carbon-based materials for sustainable and biodegradable power sources.
Related papers:
Heterogeneous Copper(0)-Assisted Dopamine Oxidation: A New Pathway to Controllable and Scalable Polydopamine Synthesis.