Supercapacitors
Continuous development and modification of active electrode materials and electrolytes are essential to develop high energy density supercapacitors. At MCRG, we use various materials such as Mxenes, conducting polymers, reduced graphene oxide and other composite materials to fabricate electrodes for supercapacitor applications. Our main focus is:
- Synthesis of Electrode Materials: We employ chemical and electrochemical techniques for the synthesis of various conducting materials. One part of the research is focused on the chemical synthesis of 2-dimensional materials such as Titanium carbide, reduced graphene oxide and its composites. Additionally we also do large scale synthesis of various conducting polymers.
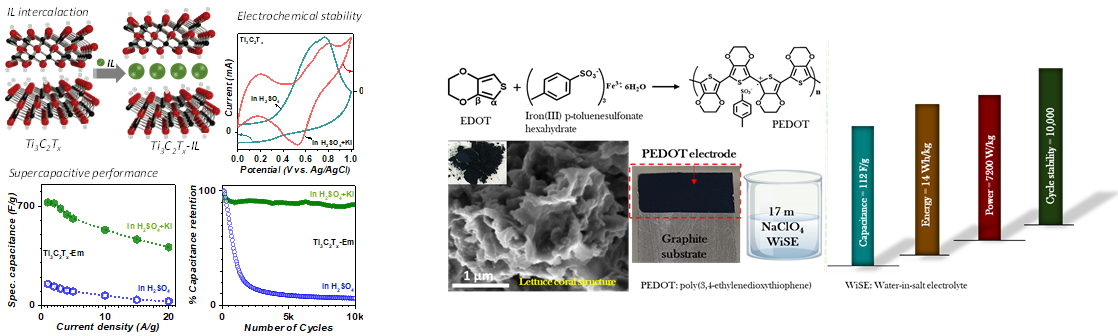
- Study of redox electrolytes: Mxenes, specifically Titanium carbide is a 2-d materials that has been widely used for energy storage applications. However so far, the materials show electrochemical instability in anodic potentials. Our Mxene research focuses on the use of various acidic electrolytes along with organic and inorganic redox molecules to achieve anodic stability and high capacitance values for MXene based 2-electrode systems.
- Water-in-Salt Electrolytes (WiSE) : A major focus of our research is enhancing the energy density of supercapacitors. WiSE’s have emerged as a primary preference for aqueous supercapacitors owing to their wide electrochemical stability window.
Related papers:
Wide electrochemical stability window of NaClO4 water-in-salt electrolyte elevates the supercapacitive performance of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene).
Supercapacitive performance of ionic-liquid-intercalated two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx in redox electrolyte.